

< Previous | Contents | Next >
Annex 2-3 Guidance for surface inspection of cast steel crankshafts
1. Application
(1) This Guidance provides for the surface inspection of the cast steel crankshaft to be carried out on completion of machining (for shrunk parts, before shrinkage).
(2) The surface inspection is to be carried out by the methods specified in 3. Where defects were found as a result of the inspection, the Surveyor is to decide pass or rejection of the crankshaft
by the standards for allowable limit of defects prescribed in 6.
(3) The inspection during the intermediate stage under construction is to be carried out actively by the manufacturer. The inspection methods are prescribed in 4.
(4) NDE personnel requirements and inspection plans are to comply with the requirements specified in Annex 2-2, 2 and 4 (2) (a) of this Guidance.
2. Divisions for inspection surface
The inspected surface of the crankshaft is divided into the following I to IV zones as shown in
Fig 1. The inspection methods and standards are specified depending on the zones respectively.
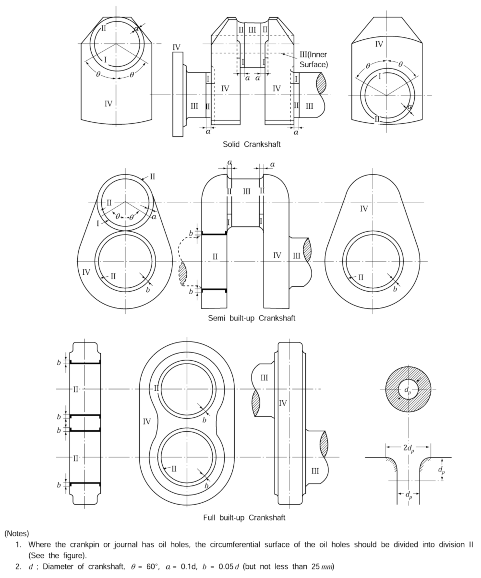
Fig 1 Divisions for Inspection Surface
![]()
Guidance Relating to the Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015 57
![]()
3. Methods of inspection
(1) The surface is to be inspected as under in accordance with Divisions for inspection surface prescribed in 2. But where CC defects (refer to Table 1) have been detected as a result of the inspection, the Surveyor may demand ultrasonic inspection additionally.
Kinds | Inspections |
Zone I and II | Magnetic particle inspection or dye penetrant inspection |
Zone III and IV | Visual inspection |
(Notes)
1. Regarding the parts used as forged or cast condition, it is to be subjected to magnetic particle inspection notwithstanding the above requirement.
2. Regarding the Zone III of the crankshaft to which quenching and tempering heat treat- ments are applied, or the same zone of the crankshaft to which surface hardening treat- ment is applied, it is to be subjected to either magnetic particle inspection or dye pene- trant inspection notwithstanding the above requirement.
![]()
(2) The methods of magnetic particle inspection, dye penetrant inspection and visual inspection are to be as deemed appropriate by the Society.
4. Inspection during intermediate stage
(1) The manufacturer is recommended to carry out actively ultrasonic inspection for the crankshaft at the appropriate stage during the manufacturing process and prove that the crankshaft has no harmful defects internally.
(2) The manufacturer should carry out actively the surface inspection at each stage under production. As the results when harmful defects of the material were found, the manufacturer is
to inform the Surveyor of the facts and obey his instruction. Regarding cast steel crankshafts,
when accepted by the Surveyor, defects can be remedied by welding according to the Annex 2-4.
(3) Regarding the crankshaft which surface hardening treatment is taken, the manufacturer is actively to inspect the surface. The records of surface inspection are to be submitted to the Surveyor when he requires.
5. Standards for surface inspection
(1) When defects have been detected as a result of the surface inspection prescribed in 3, pass or rejection is to be decided by the following 6, considering the results of the inspection of 4. But even those which have failed to comply with these limits may be taken as passed, if in
consideration with the position, size, direction and nature of the defects as well as the shape
and dimension of such crankshafts, and the Surveyor accepted justifiable. Conversely, even those which have complied with these limits would be disqualified if they should contain such numer- ous defects as to make them unsuitable as crankshaft from the nature, distribution and direction
of the defects.
(2) The treatment of defects for surface inspection is to be as the followings:
(A) The lengths of the defects in the Standards are the actual lengths appeared by visual inspection.
(B) The defects can be removed after acceptance of the Surveyor.
(C) Removal of defects is to be carried out by grinding.
(D) Where two defects spaced less than 5 mm apart, these are to be removed regarding as one
defect.
(E) The grooves caused by removing are to be smoothly rounded off by as large radius as pos- sible toward the shaft surface.
(F) The size of grooves caused by removing means the size before rounding off
(G) Regarding cast steel crankshafts, when accepted by the Surveyor, defects can be remedied by welding according to the Annex 2-4.
(H) When defects were removed, it is to be confirmed that the defects have been completely re-
moved by magnetic particle inspection or dye penetrant inspection.
![]()
58 Guidance Relating to the Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015
![]()
(I) Regarding the crankshaft which defects are left and removed, the manufacturer is to make detailed inspection records and submit the same to the Surveyor. In these inspection records, the position, size, direction and nature of the defects on the inspected surface and the posi- tion and size of grooves caused by removing the defects is to be recorded.
6. Standards for allowable limit of defects for surface inspection
(1) Application
(a) The standards are to be applied to the semi builtup cast steel and full built up crankshafts.
(b) Defects specified in this Guidance are Grade CC shown in (B).
(2) Classification of material defects
The surface defects are classified as the following excluded from consideration by this Guidances.
Table 1, but Grade CA and CB defects are
Table 1 Classification of Material Defects
Classification | Names of defects |
Grade CA defects | Microscopic non-metal inclusion |
Grade CB defects | Pin hole and inclusion which do not exceed 0.2 mm in length |
Grade CC defects | · Exceed 0.2 mm in length, Pin-hole, blowhole, sand-inclusion, slag inclusion · Shrinkage cavity, · Hot tear, cold crack |
(3) Standards
For Standards, Table 2 is to be applied.
![]()
![]()
Table 2 Standards
Divisions | Standards |
I | All defects which are detected are to be removed. The depth of grooves caused by such removing is to be less than 0.01 . In this case, the fillet parts are to be so finished that the original shape is retained. For parallel and plane parts, the grooves are to be so rounded off that the bottom radius of the grooves is not less than three times the depth of the groove. |
II | All defects which are detected are to be removed, except the following defects: (i) Defects not exceeding 1 mm which are not crowded. (ii) Defects not exceeding 3 mm with sufficient spacing between each two. The depth of grooves caused by such removing is to be less than 0.01 , and the grooves are to be so rounded off that the bottom radius of the grooves is not less than three times the depth of the groove, and in no case it shall be less than twice the depth. |
III | All defects which are detected are to be removed, except the following defects: (i) Defects not exceeding 3 mm which are not crowded. (ii) Defects not exceeding 5 mm with sufficient spacing between each two. The depth of grooves caused by such removing is to be less than 0.01 , and the grooves are to be so rounded off that the bottom radius of the grooves is not less than twice the depth of the groove. |
IV | All defects which are detected are to be removed, except those not exceeding 8 mm. The depth of grooves caused by such removing is to be such that it does not affect the strength of the zone, and for the depth, it is necessary to receive the Surveyor's approval. |
![]()
![]()
![]()
Guidance Relating to the Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015 59
![]()